7. Deployment of User Interface#
This section provides information regarding the deployment of the BrainKB UI, both in the development and the production mode.
Note
Before proceeding with the following steps, ensure you have downloaded the BrainKB UI source code from the BrainKB UI GitHub.
Navigate to the nextjsUIapp directory, and perform the tasks described below. Currently, the latest development branch is admin-ui.
7.1. System Requirements#
The BrainKB UI is based on Node.js(open-source, cross-platform JavaScript runtime environment) , and NextJS(a react framework for creating web applications).
Installing
Node.js: check the current requirements on the https://nextjs.org/docs/getting-started/installationInstalling additional NextJS packages and creating a new app using the
Node.jspackage managernpm(this will create a new app structure and add new file, so you might want to do it in a new empty directory):npm install next@latest react@latest react-dom@latest
If you get issue with depenency, add
--legacy-peer-depsoptions.Installation of the dependencies.
npm install
Once all the NextJS requirements has been met or covered, next step is to configure the OAuth. In our case we use Google and GitHub. Therefore, you would need to obtain the OAuth client ID and secret and update the
.env.localfile (shown below). Additionally, you also need to provide the secret for NextAuth, a library that we use authentication. TheNEXTAUTH_URLfor development ishttp://localhost:3000. Similarly, the GitHub secret and client ID can be obtained from GitHub at settings/tokens and Google at https://console.cloud.google.com/.#OAuth credentials GITHUB_CLIENT_ID= GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET= GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID= GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET= #Auth Config NEXTAUTH_SECRET= NEXTAUTH_URL= # Query service API configuration NEXT_PUBLIC_API_ADMIN_HOST= #endpoint, e.g., query that will be invoked when running SPARQL query NEXT_PUBLIC_API_QUERY_ENDPOINT=
Note: For Google OAuth, unless the
Publishing statusispublished, it will beTestingas shown in Fig. 7.1. Since this is in a testing mode, only the testing users can log in via Google OAuth.If the
User typeisInternal, only the organizational members can log in (e.g., *.mit.edu).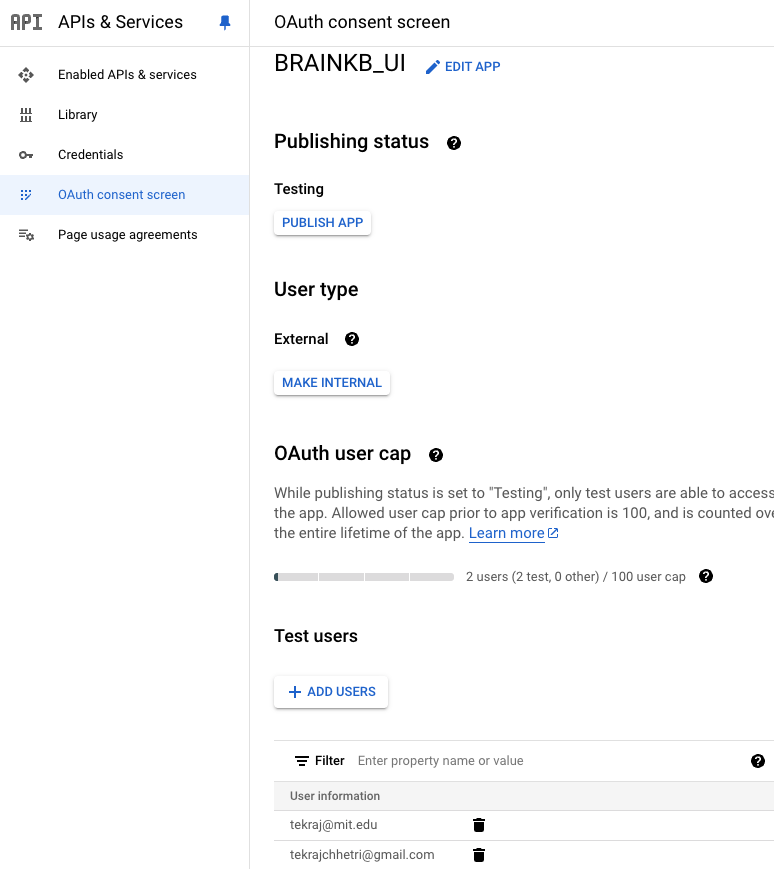
Fig. 7.1 Google OAuth setup.#
The next step is to configure the
config-home.yamlandconfig-knowledgebases.yamlinsidecomponentsdirectory. Theconfig-home.yamlis use to configure the home (or landing) page andconfig-knowledgebases.yamlis use to configure theknowledge basepage. Fig. 7.2 and Fig. 7.3 show the configuration of the BrainKB UI landing page header using theconfig-home.yamlfile. Similarly, Fig. 7.4 shows the configuration of theknowledge basepage usingconfig-knowledgebases.yamland the mappings of the configuration files into different UI compoentns ofknowledge basepage.Configuration Files section provides further details on the configuration files used in BrainKB UI.
Important
In order to apply the BrainKB UI to your specific use cases, you will need to modify the configuration files (refer to Section Configuration Files) as per your requirements.
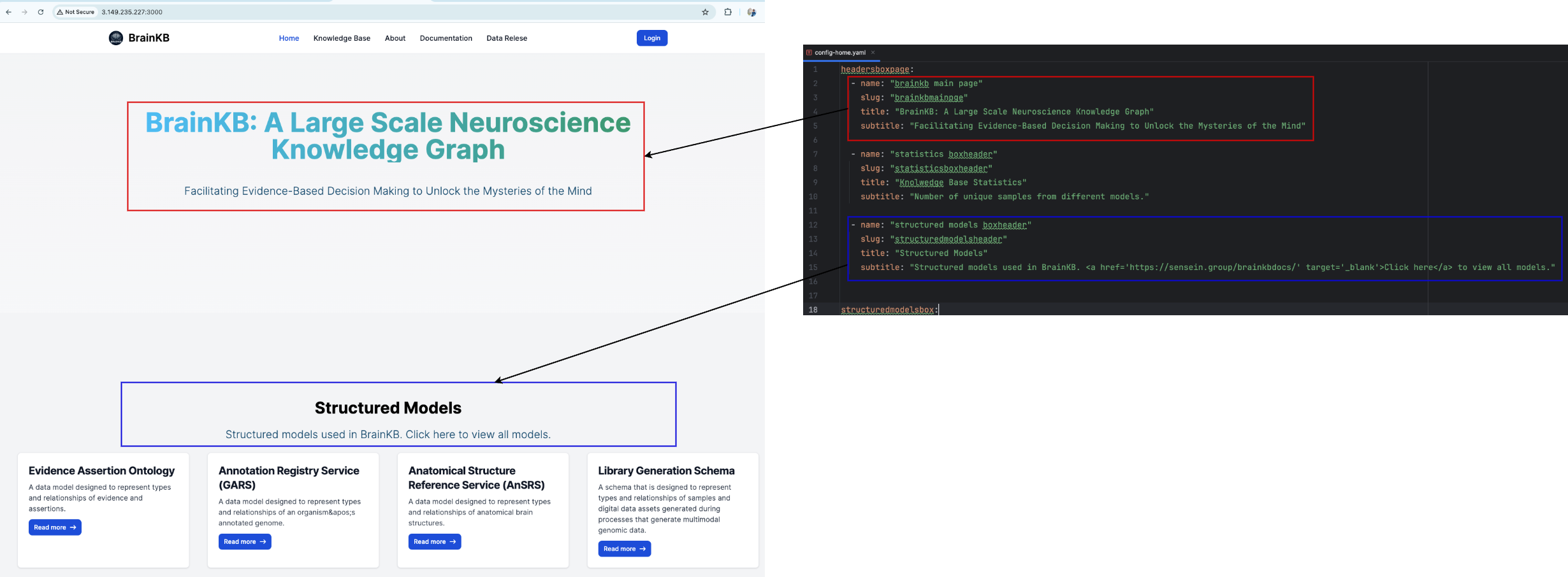
Fig. 7.2 Landing page header configuration using
config-home.yaml.#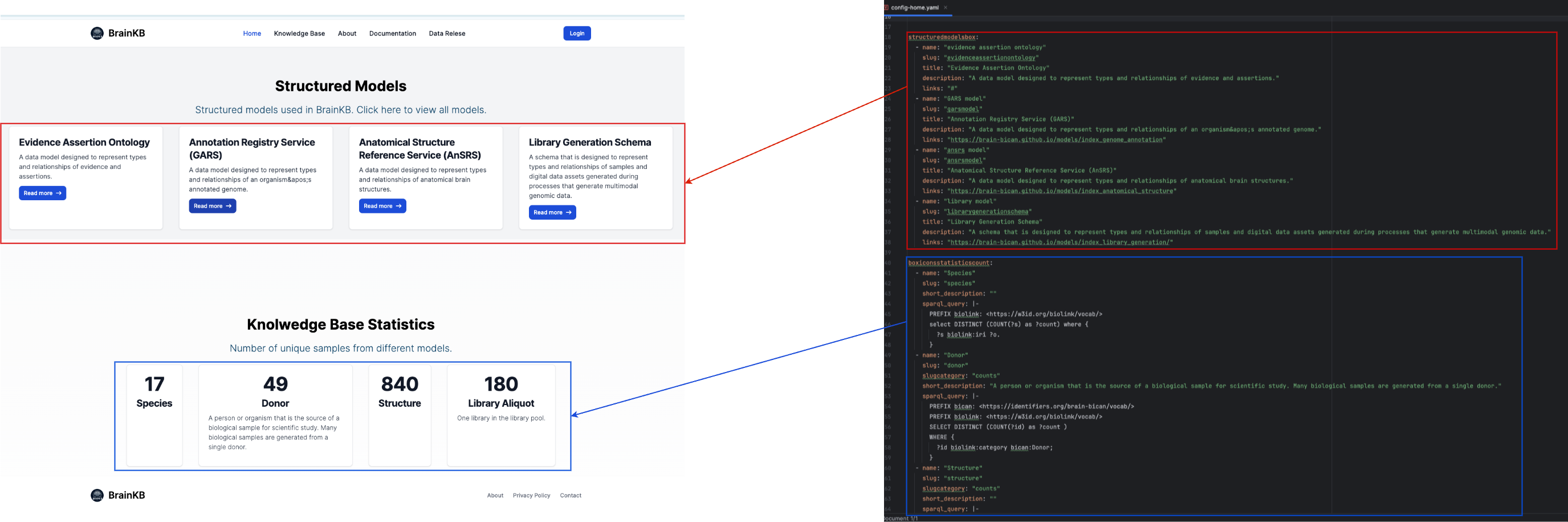
Fig. 7.3 Landing page configuration of structured models and statics cards using
config-home.yaml.#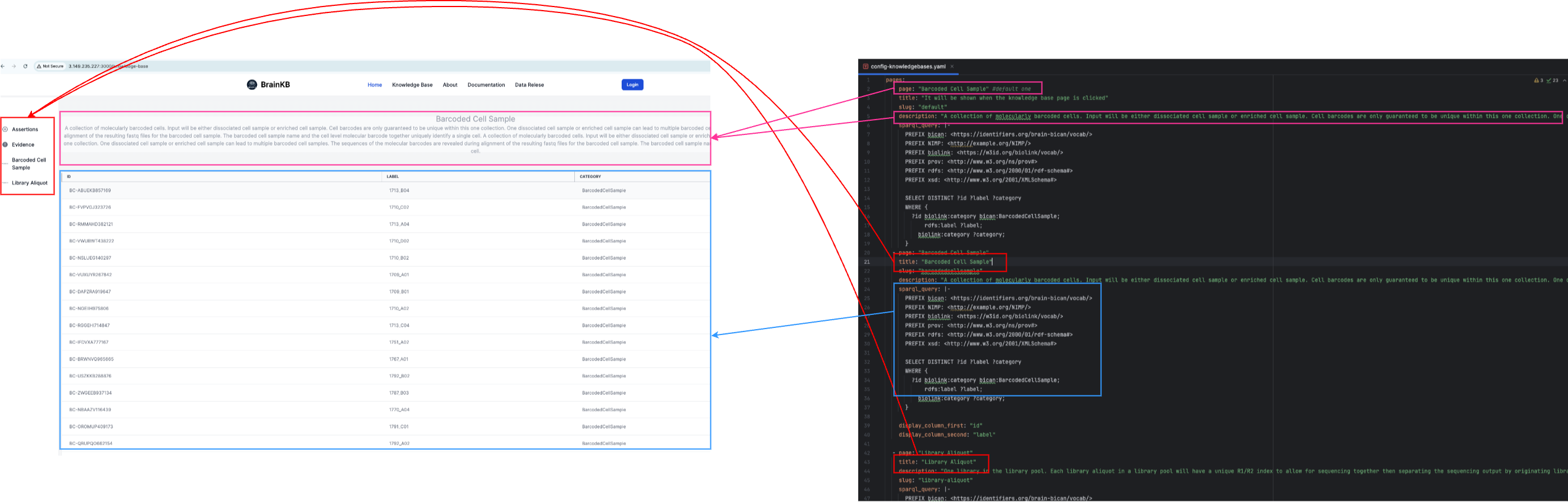
Fig. 7.4 Configuration of the knowledge base page using
config-knowledgebases.yaml.#
7.2. Running in Non-Containerized Development Mode#
You can run the application either using npm or next command as follows.
Using
npmnpm run devUsing
nextnext dev
7.3. Running in Non-Containerized Production Mode#
To run in a production mode first you need to build the application and start. Run the following command in order.
next buildnext start
7.4. Running in Containerized Mode#
You can run the BrainKB UI in the containerized mode. In order to be able to run in the containerized mode, you need to install the requisite prerequisites listed below.
Docker installed on your machine.
Docker Compose installed on your machine to use the docker-compose.yml file. After installing the necessary prerequisites, navigate to
nextjsUIappdirectory and rundocker compose upcommand.
Upon successful run, you should see following (see Fig. 7.5), and you would be able to browse the deployed UI at http://localhost:3000.
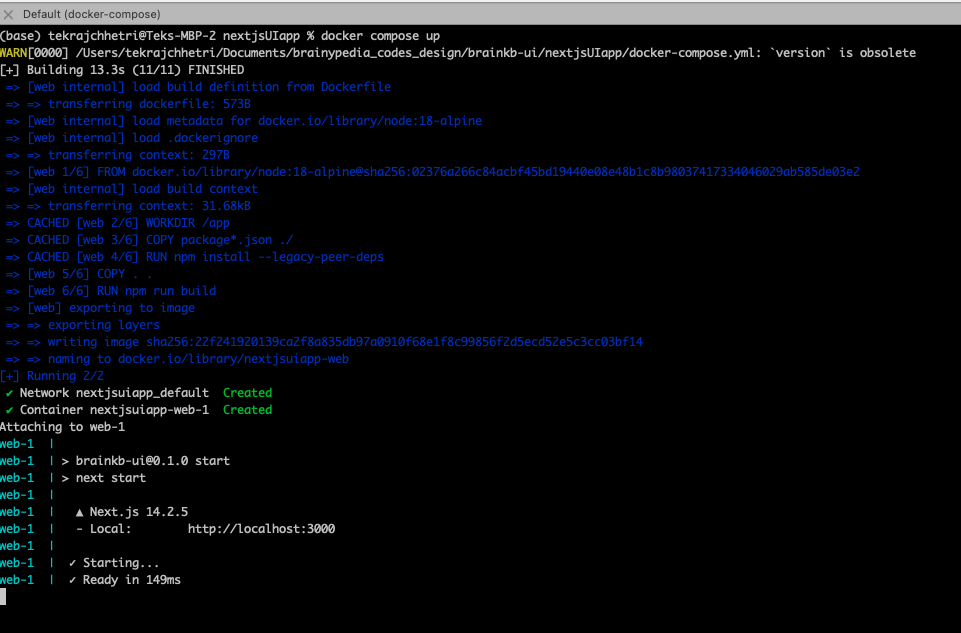
Fig. 7.5 Running in Containerized mode.#
However, if port 3000 is already in use on your host machine, you can change the port mapping in the docker-compose.yml file as shown in the docker compose file below. For example, you can modify the file to use a different host port, such as 4000. Please note that inside the Docker container, the application will continue to run on port 3000, but it will be accessible on the new port you specified on the host machine. This way, you can browse the UI on the updated port without conflicts.
version: '3'
services:
web:
build: .
ports:
- '4000:3000'
environment:
- NODE_ENV=production
volumes:
- .:/app
- /app/node_modules
- /app/.next
To run in the development mode, change the value of NODE_ENV=development.
7.5. Configuration Files#
BrainKB is designed to be configurable so that it can be easily reusable in other use cases. To make the BrainKB UI reusable, we have adopted a configure file approach using YAML-based configuration files (or LinkML schemas (or ontologies) expressed in YAML). In the subsections below, we describe different configuration files and schemas that are used in BrainKB UI.
Note
Some of the parameters (or variables) in the configuration files are not used as of now (there’s a plan to use) and therefore, descriptions are not available. The descriptions will be updated as they are used or will be removed in case they are not used.
7.5.1. config-home.yaml#
The config-home.yaml file is used to configure the home page, aka the landing page. The configuration file shown below is the default one that is being used in the current implementation.
The following is a description of the various components of the configuration files.
headersboxpage: The configuration details for the titles and subtitles of various sections of the landing page.
name: The human readable name. Is not used in the UI.slug: A unique component is used to identify the particular headerbox.title: The title text that you wish to appear in the UI.subtitle: The subtitle text that you wish to appear in the UI.
structuredmodelsbox: The configuration for the schema (or ontology) information.
name: The human readable name. Is not used in the UI.slug: A unique component is used to identify the particular card (or box).title: The title text for the card (or box) that you wish to appear in the UI.description: The short description that you wish to appear in the UI.links: The navigation link for the models (or schemas) documentation page.
boxiconsstatisticscount: The configuration for the knowledge base statistics.
name: The human readable name. Is not used in the UI.slug: A unique component is used to identify the particular card (or box).short_description: The short description that you wish to appear in the UI.sparql_query: The SPARQL query that is to be executed to get the statistics.
headersboxpage:
- name: "brainkb main page"
slug: "brainkbmainpge"
title: "BrainKB: A Large Scale Neuroscience Knowledge Graph"
subtitle: "Facilitating Evidence-Based Decision Making to Unlock the Mysteries of the Mind"
- name: "statistics boxheader"
slug: "statisticsboxheader"
title: "Knolwedge Base Statistics"
subtitle: "Number of unique samples from different models."
- name: "structured models boxheader"
slug: "structuredmodelsheader"
title: "Structured Models"
subtitle: "Structured models used in BrainKB. <a href='https://sensein.group/brainkbdocs/' target='_blank'>Click here</a> to view all models."
structuredmodelsbox:
- name: "evidence assertion ontology"
slug: "evidenceassertionontology"
title: "Evidence Assertion Ontology"
description: "A data model designed to represent types and relationships of evidence and assertions."
links: "#"
- name: "GARS model"
slug: "garsmodel"
title: "Annotation Registry Service (GARS)"
description: "A data model designed to represent types and relationships of an organism's annotated genome."
links: "https://brain-bican.github.io/models/index_genome_annotation"
- name: "ansrs model"
slug: "ansrsmodel"
title: "Anatomical Structure Reference Service (AnSRS)"
description: "A data model designed to represent types and relationships of anatomical brain structures."
links: "https://brain-bican.github.io/models/index_anatomical_structure"
- name: "library model"
slug: "librarygenerationschema"
title: "Library Generation Schema"
description: "A schema that is designed to represent types and relationships of samples and digital data assets generated during processes that generate multimodal genomic data."
links: "https://brain-bican.github.io/models/index_library_generation/"
boxiconsstatisticscount:
- name: "Species"
slug: "species"
short_description: ""
sparql_query: |-
PREFIX biolink: <https://w3id.org/biolink/vocab/>
select DISTINCT (COUNT(?s) as ?count) where {
?s biolink:iri ?o.
}
- name: "Donor"
slug: "donor"
short_description: "A person or organism that is the source of a biological sample for scientific study. Many biological samples are generated from a single donor."
sparql_query: |-
PREFIX bican: <https://identifiers.org/brain-bican/vocab/>
PREFIX biolink: <https://w3id.org/biolink/vocab/>
SELECT DISTINCT (COUNT(?id) as ?count )
WHERE {
?id biolink:category bican:Donor;
}
- name: "Structure"
slug: "structure"
short_description: ""
sparql_query: |-
PREFIX bican: <https://identifiers.org/brain-bican/vocab/>
SELECT DISTINCT (COUNT (?id) as ?count)
WHERE {
?id bican:structure ?o;
}
- name: "Library Aliquot"
slug: "libraryaliquot"
short_description: "One library in the library pool."
sparql_query: |-
PREFIX bican: <https://identifiers.org/brain-bican/vocab/>
PREFIX biolink: <https://w3id.org/biolink/vocab/>
SELECT DISTINCT (COUNT(?id) as ?count )
WHERE {
?id biolink:category bican:LibraryAliquot;
}
7.5.2. config-knowledgebases.yaml#
The config-knowledgebases.yaml file is used to configure the knowledge base, aka the landing page. The configuration file shown below is the default one that is being used in the current implementation.
The following is a description of the various components of the configuration files.
pages: The configuration information for various knowledge base pages.
page: The text that will appear on the top of the page.title: The text that will appear on the left side menu, except the one with thedefaultslug.slug: A unique component is used to identify the particular page. Note: The slugdefaultis a special one. The page marked withdefaultslug will be displayed as a default knowledge base page upon clicking theknowledge basemenu.description: The description that you wish to appear on the page.sparql_query: The SPARQL query that is to be executed to get the statistics.
Fig. 7.6 shows the mapping of the page configurations.
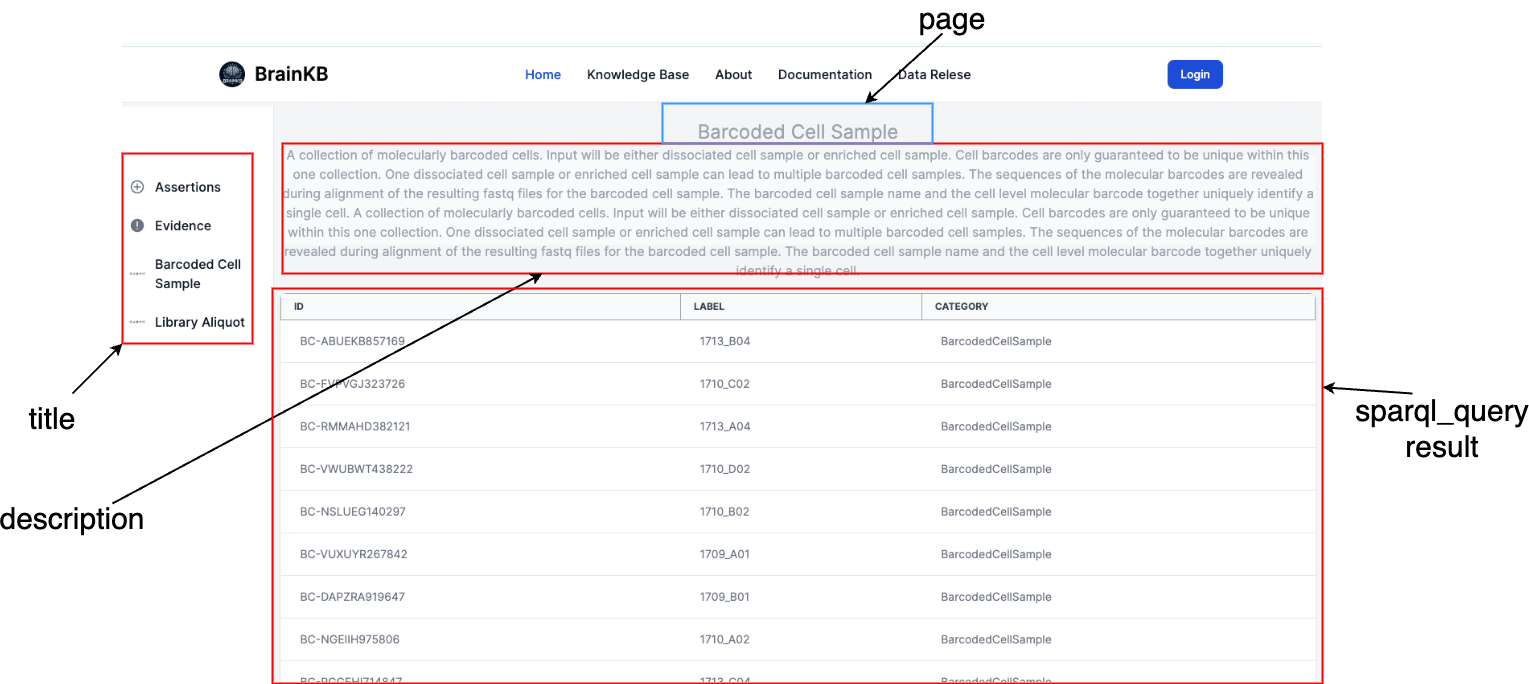
Fig. 7.6 Mapping of different configuration components into a knowledge base page UI.#
pages:
- page: "Barcoded Cell Sample" #default one
title: "It will be shown when the knowledge base page is clicked"
slug: "default"
description: "A collection of molecularly barcoded cells. Input will be either dissociated cell sample or enriched cell sample. Cell barcodes are only guaranteed to be unique within this one collection. One dissociated cell sample or enriched cell sample can lead to multiple barcoded cell samples. The sequences of the molecular barcodes are revealed during alignment of the resulting fastq files for the barcoded cell sample. The barcoded cell sample name and the cell level molecular barcode together uniquely identify a single cell. A collection of molecularly barcoded cells. Input will be either dissociated cell sample or enriched cell sample. Cell barcodes are only guaranteed to be unique within this one collection. One dissociated cell sample or enriched cell sample can lead to multiple barcoded cell samples. The sequences of the molecular barcodes are revealed during alignment of the resulting fastq files for the barcoded cell sample. The barcoded cell sample name and the cell level molecular barcode together uniquely identify a single cell."
sparql_query: |-
PREFIX bican: <https://identifiers.org/brain-bican/vocab/>
PREFIX NIMP: <http://example.org/NIMP/>
PREFIX biolink: <https://w3id.org/biolink/vocab/>
PREFIX prov: <http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#>
PREFIX rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#>
PREFIX xsd: <http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#>
SELECT DISTINCT ?id ?label ?category
WHERE {
?id biolink:category bican:BarcodedCellSample;
rdfs:label ?label;
biolink:category ?category;
}
- page: "Barcoded Cell Sample"
title: "Barcoded Cell Sample"
slug: "barcodedcellsample"
description: "A collection of molecularly barcoded cells. Input will be either dissociated cell sample or enriched cell sample. Cell barcodes are only guaranteed to be unique within this one collection. One dissociated cell sample or enriched cell sample can lead to multiple barcoded cell samples. The sequences of the molecular barcodes are revealed during alignment of the resulting fastq files for the barcoded cell sample. The barcoded cell sample name and the cell level molecular barcode together uniquely identify a single cell. A collection of molecularly barcoded cells. Input will be either dissociated cell sample or enriched cell sample. Cell barcodes are only guaranteed to be unique within this one collection. One dissociated cell sample or enriched cell sample can lead to multiple barcoded cell samples. The sequences of the molecular barcodes are revealed during alignment of the resulting fastq files for the barcoded cell sample. The barcoded cell sample name and the cell level molecular barcode together uniquely identify a single cell."
sparql_query: |-
PREFIX bican: <https://identifiers.org/brain-bican/vocab/>
PREFIX NIMP: <http://example.org/NIMP/>
PREFIX biolink: <https://w3id.org/biolink/vocab/>
PREFIX prov: <http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#>
PREFIX rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#>
PREFIX xsd: <http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#>
SELECT DISTINCT ?id ?label ?category
WHERE {
?id biolink:category bican:BarcodedCellSample;
rdfs:label ?label;
biolink:category ?category;
}
display_column_first: "id"
display_column_second: "label"
- page: "Library Aliquot"
title: "Library Aliquot"
description: "One library in the library pool. Each library aliquot in a library pool will have a unique R1/R2 index to allow for sequencing together then separating the sequencing output by originating library aliquot through the process of demultiplexing. The resulting demultiplexed fastq files will include the library aliquot name. A given library may produce multiple library aliquots, which is done in the case of resequencing. Each library aliquot will produce a set of fastq files."
slug: "library-aliquot"
sparql_query: |-
PREFIX bican: <https://identifiers.org/brain-bican/vocab/>
PREFIX NIMP: <http://example.org/NIMP/>
PREFIX biolink: <https://w3id.org/biolink/vocab/>
PREFIX prov: <http://www.w3.org/ns/prov#>
PREFIX rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#>
PREFIX xsd: <http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#>
SELECT DISTINCT ?id ?label ?category
WHERE {
?id biolink:category bican:LibraryAliquot;
rdfs:label ?label;
biolink:category ?category;
}
default_kb: false
display_column_first: "id"
display_column_second: "label"
display_column_third: "category"
7.6. Known Issues#
OAuth: Especially with the Google based authentication, even after successful setup, you might get error regarding mismatch redirect URI, as shown in Fig. 7.7, thereby preventing you to log in. This is because unlike GitHub-based OAuth, where you can redirect to the pages that one desire, e.g., home page, the redirect URI in case of Google needs to be specific.
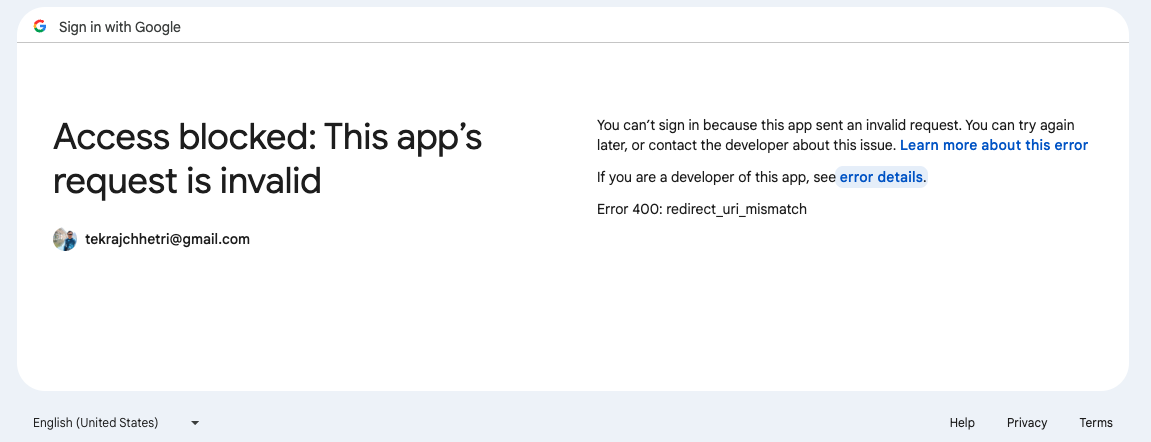
Fig. 7.7 Unable to login with Google.#
To fix this issue, set the redirect URI as
https://{YOUR_DOMAIN}/api/auth/callback/google. InYOUR_DOMAINis:https://localhost:3000/api/auth/callback/googledevelopment modein production, replace
YOUR_DOMAINwith registered domain name
More information regarding these callbacks can be obtained from NextJS website at https://next-auth.js.org/providers.